There is a growing need for accurate calibration of high-precision electrical and mechanical stages
used for metrology, ratio frequency measurements, integrated circuits and high-tech manufacturing.
The decreasing feature sizes and decreasing tolerance for errors in, for example, semiconductor
manufacturing make accurate calibration and its maintenance essential.
The problem arises because modern manufacturing and measuring instruments are so precise, with
repeatability in nanometers, that there are no standard measurement grids of comparable accuracy
with which to calibrate them. A promising and mathematically rigorous approach for calibrating
high-precision stages uses the stage to calibrate itself. This approach appears to offer many
advantages, including the possibility of standardizing measurements of accuracy.
A self-calibrated measuring method is based on a self-calibration with the use of internal
reference elements and quantities. After the self-calibration the measuring errors are automaticlly
corrected by digital signal processing algorithms, so that the measuring accuracy of the resulted
measuring system can be improved in comparison with that of the original measuring system.
For measuring systems with a linear input-output relation, two reference elements are usually
used for the self-calibration. The measuring result is determined by a linear interpolation using
the measuring and reference data of the self-calibration.
For measuring systems with a nonlinear input and output relation, the self-calibration needs three
reference elements. The measuring result is determined by a quadratic interpolation. The measuring
errors are compensated by the interpolation. Therefore, the measuring accuracy of a self-calibrated
measuring system depends only on the the tolerance of the reference elements, normally better than 0.1%.
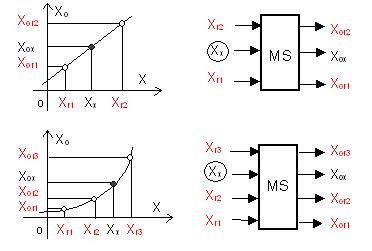 |
Linear Interpolated Self-Calibration (LISC)
- System with a linear relation
- Two reference quantities Xr1 and Xr2
- Linear interpolation
Quadratic Interpolated Self-Calibration (QISC)
- System with a nonlinear relation
- Three reference quantities Xr1,Xr2,Xr3
- Quadratic Interpolation
|
This measuring method can be used for measurements of electrical, geometrical and mechanical
quantities. As example the following figures show a simple self-calibrated impedance measuring system.
For the self-calibration reference resistors are used in this system. During the self-calibrattion
the reference resistors are measured with the impedance measuring instrument. The measuring result
is determined with a linear or quadratic interpolation with the use of measuring and reference data.
The measuring errors are compensated by the self-calibration methods.
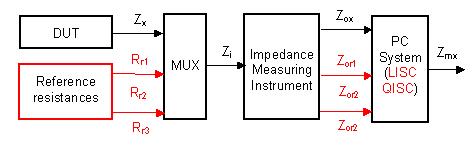 Fig. 2 Self-calibrated impedance measuring system of elements and analog circuits
Fig. 2 Self-calibrated impedance measuring system of elements and analog circuits
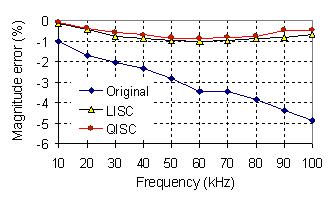
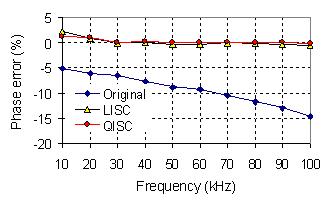
Fig. 3 Accuracy improvement of the impedance measurement of an analog circuit
using the
self-calibrated measuring methods
|